What are the differences between heat pump, vented and condenser tumble dryers?
There are three main types of tumble dryers: condenser tumble dryers, heat pump tumble dryers and vented tumble dryers. The main difference between these appliances is the way each model extracts hot air:.
- Vented tumble dryers expel hot air through an external vent
- Condenser tumble dryers convert hot air into water, ready to be removed by the user
- Heat pump tumble dryers reuse the hot air they generate, keeping energy consumption to a minimum
Are you unsure which type of tumble dryer is right for you? This handy guide from Beko will walk you through the options and help you make a confident, informed choice.

What is a vented tumble dryer?
Vented tumble dryers expel hot air through an external vent. While this setup can help keep utility bills low, since the appliance doesn’t convert hot air into water, it does come with some limitations in flexibility and installation.
When purchasing a vented tumble dryer, bear in mind that you must make sure that there is a suitable location in your house for the appliance. The dryer needs to be installed near an external vent that has been fitted into an external wall, allowing the damp air to escape outside.
Thanks to the use of an external vent though, there’s no need to manually empty a water tank, though this convenience comes at the cost of less installation flexibility.
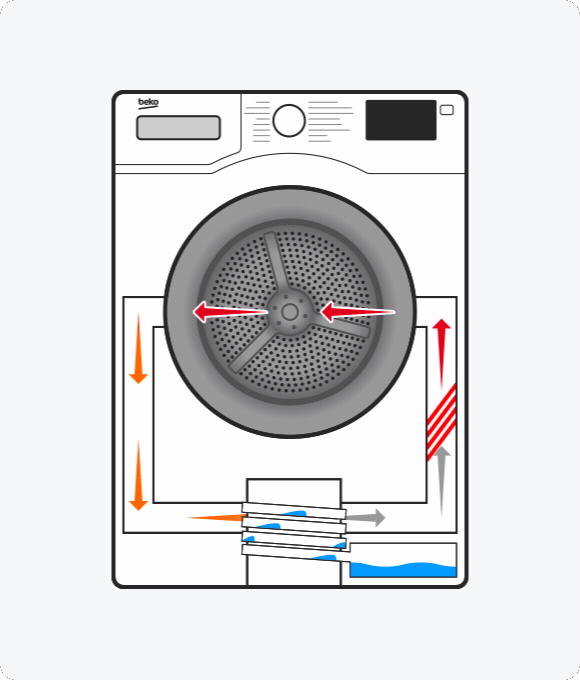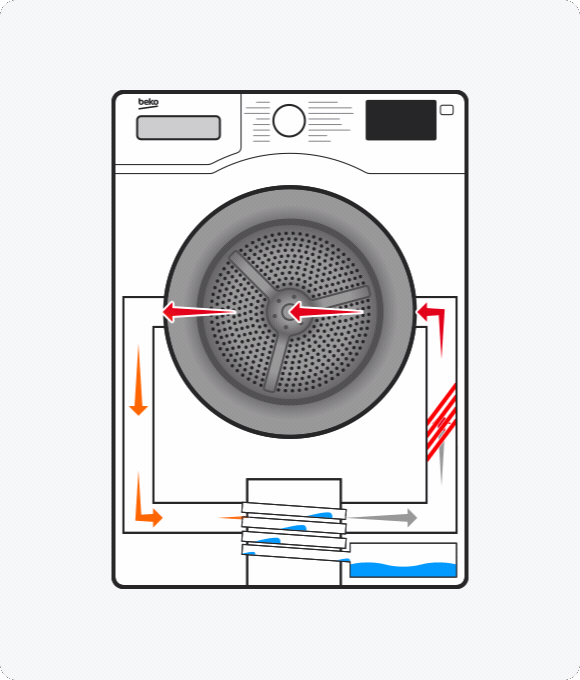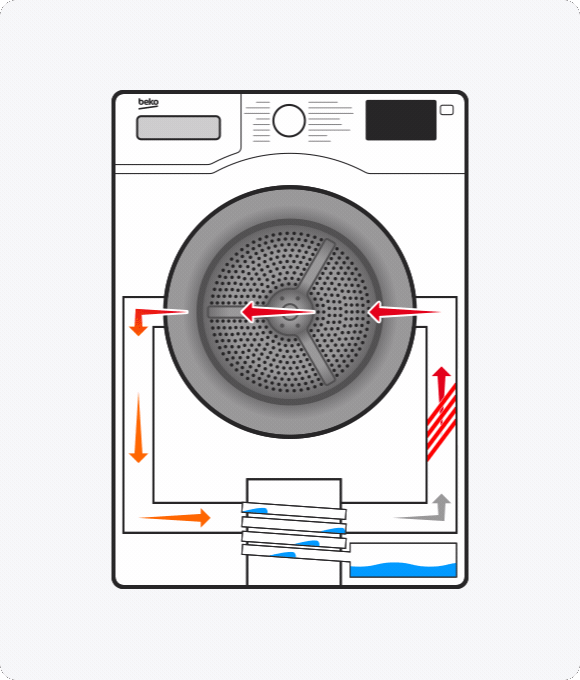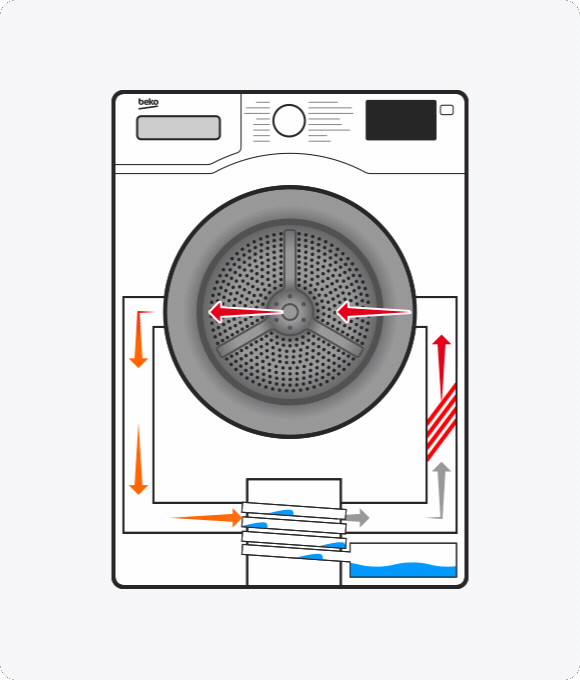
What is a heat pump tumble dryer?
Heat pump tumble dryers uses a closed-loop heat exchange system that dry clothes at a lower temperature, offering gentler care and better protection for your laundry.
Although drying times are slightly longer when compared to condenser tumble dryers, heat pump tumble dryers offer great energy savings and will keep your utility bills to a minimum.
A heat pump dryer uses hot air to absorb moisture from your clothes. After this air passes through the drum, it goes through the evaporator, which removes the moisture. This is then collected and stored in a tank. The remaining air is reheated and used to continue drying your clothes.
While both condenser and vented tumble dryers release the hot air used to dry clothes, heat pump technology reuses it.
Key advantages of a heat pump tumble dryer include:
- Flexible installation: Heat pump tumble dryers do not need to be installed near an external wall, making them much easier to fit anywhere within your home
- Energy efficiency: They consume significantly less energy than condenser or vented models, which leads to notable savings on your utility bills over time
- Quieter performance: Heat pump dryers typically operate at lower noise levels than other dryer types, especially when equipped with a ProSmart™ Inverter Motor, making them ideal for open-plan homes
- Gentle on clothes: Drying at lower temperatures helps protect delicate fabrics from shrinking, fading, or damage, making heat pump dryers ideal for caring for everyday garments and more sensitive laundry items
A selection of our heat pump tumble dryers feature our RapiDry™ technology too. This gives you the option to dry your clothes on a shorter cycle, even when compared to condenser dryers, while still maintaining a high energy efficiency. So, you can achieve perfectly dry clothes in less time.
Whilst it should be noted that the programmes on a heat pump dryer do take longer than condenser dryers, this can still fit easily into your laundry routine.
See heat pump tumble dryers
What is a condenser tumble dryer?
Condenser tumble dryers do not need an externally vented hose, meaning you will be able to install your appliance anywhere in your home.
However, a condenser dryer does need a constant supply of cool air to function. When installing your appliance, make sure you place the dryer in a well-ventilated room, where warm air can easily escape.
Key advantages of a condenser tumble dryer include:
- Flexible installation: Condenser tumble dryers do not need to be installed near an external wall, making them much easier to fit anywhere within your home
- Sensor programmes: Many models feature moisture sensors that automatically stop the cycle when items reach the selected dryness level, protecting fabrics and saving energy
- Quick programmes: Some Beko condenser dryers include fast-drying options like the Quick Dry programme, which can dry a small load (e.g. 1?kg) in as little as 15–30 minutes, ideal for when you need an outfit in a hurry.
A condenser tumble dryer does use high temperatures to dry your clothes though, reaching a maximum temperature of 70-75°C. In comparison, the maximum temperature reached in a heat pump tumble dryer is 50°C.
Although the drying times for cycles in condenser tumble dryers are shorter than cycles in heat pump dryers, the high temperature combined with the expulsion of hot air means the appliance uses significantly more energy.
See condenser dryersHeat pump vs condenser dryers
Both a heat pump tumble dryer and a condenser dryer are designed to dry clothing efficiently. However, the main difference between the two is how they generate heat to do the job.
A condenser dryer, which is what a large portion of customers are used to, uses a heater element to generate heat, which dries clothing. When compared to a heat pump dryer, a condenser dryer can be costly and is less energy efficient.
Using a closed-loop heat exchange system, heat pump tumble dryers dry clothes at a lower temperature, keeping energy usage low and providing better protection for your laundry.
While both condenser dryers and vented tumble dryers release the hot air used to dry clothes, heat pump technology conserves and reuses it. Using a lower temperature to dry clothes, a heat pump tumble dryer also offers better protection for your clothes. Although it takes slightly longer to dry a load, compared to a standard condenser dryer, it can help to significantly reduce your energy consumption. Check out our in-depth tumble dryer buying guide to find all the information you need on capacity, sizes, energy ratings and more.
Alternatively, browse our range of tumble dryers here.
If you’ve already selected a tumble dryer, have you considered which washing machine would best suit your everyday washing needs? Explore our range of washing machines here.
Key differences between heat pump, vented and condenser tumble dryers
| Vented | Heat Pump | Condenser | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency Class | Typically C – D energy rating (least efficient) | A+ - A++ energy rating (most efficient) | B energy rating (moderately efficient) | ||
| Installation | Need external ventilation | Flexible installation (no vent needed) | Flexible installation (no vent needed) | ||
| Maintenance | No water container to empty | Water tank must be emptied regularly (unless appliance is connected directly to drainage) | Water tank must be emptied regularly (unless appliance is connected directly to drainage) | ||
| Annual energy consumption (KWh) | - | 7kg | 211.4-242.6 | 7kg | 504.2 |
| 8kg | 236-265 | 8kg | 561-619 | ||
| 9kg | 194.4-287.4 | 9kg | 615.7 | ||
| 10kg | 210.6-281.9 | 10kg | 670.6-670.9 | ||
| 12kg | 325.5 | 12kg | - | ||
Are you still unsure if a vented, condenser or heat pump tumble dryer will be best for your home? Be sure to check out our in-depth tumble dryer buying guide to find all the information you need on capacity, sizes and more. And if you’re wondering where you can place a condenser dryer in your home, see our guide here.
Alternatively, browse our fantastic range of tumble dryers if you now know the type you require. You will find that these household appliances are packed with handy features.
If you’ve already selected a tumble dryer, have you considered which washing machine would also best suit your everyday washing needs? Explore our selection of washing machines here.
Did we answer your question?
We are so sorry we were unable to answer your question. You might be able to find the answer you are looking for in the ‘Related Questions’ below. If your query is still unanswered, please head over to our Contact Us page for further assistance.
Search FAQ’s
Search or browse our frequently asked questions to find the answer to your query.




